
- Markets
- Solutions
- Services
- Innovations
- Resources
- About Us
- Careers
- Contact Us
ITIL is the acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, which is a framework that encompasses a set of best practices for delivering IT services. ITIL framework provides a standardized approach to building and managing stable IT Infrastructure that offers lesser risks, higher efficiency, and scalability for growth.
As one of the most popular and widely accepted frameworks for IT service management today, organizations use the best practices laid down by ITIL to increase operational efficiency and IT service improvement. The nucleus of ITIL is structured around a Service Lifecycle that consists of the five phases mentioned below:
In a practical scenario, organizations use a systematic approach to select, plan, support, and deliver IT services. However, it is easier said than done since it is a herculean task for an organization to align itself with business. In the real world, it is not simple to offer quality service to customers amongst constraints such as unplanned change management, less proactive helpdesks, and less comprehensive SLAs that lack clarity.
The ITIL framework is divided into five broad stages or categories:
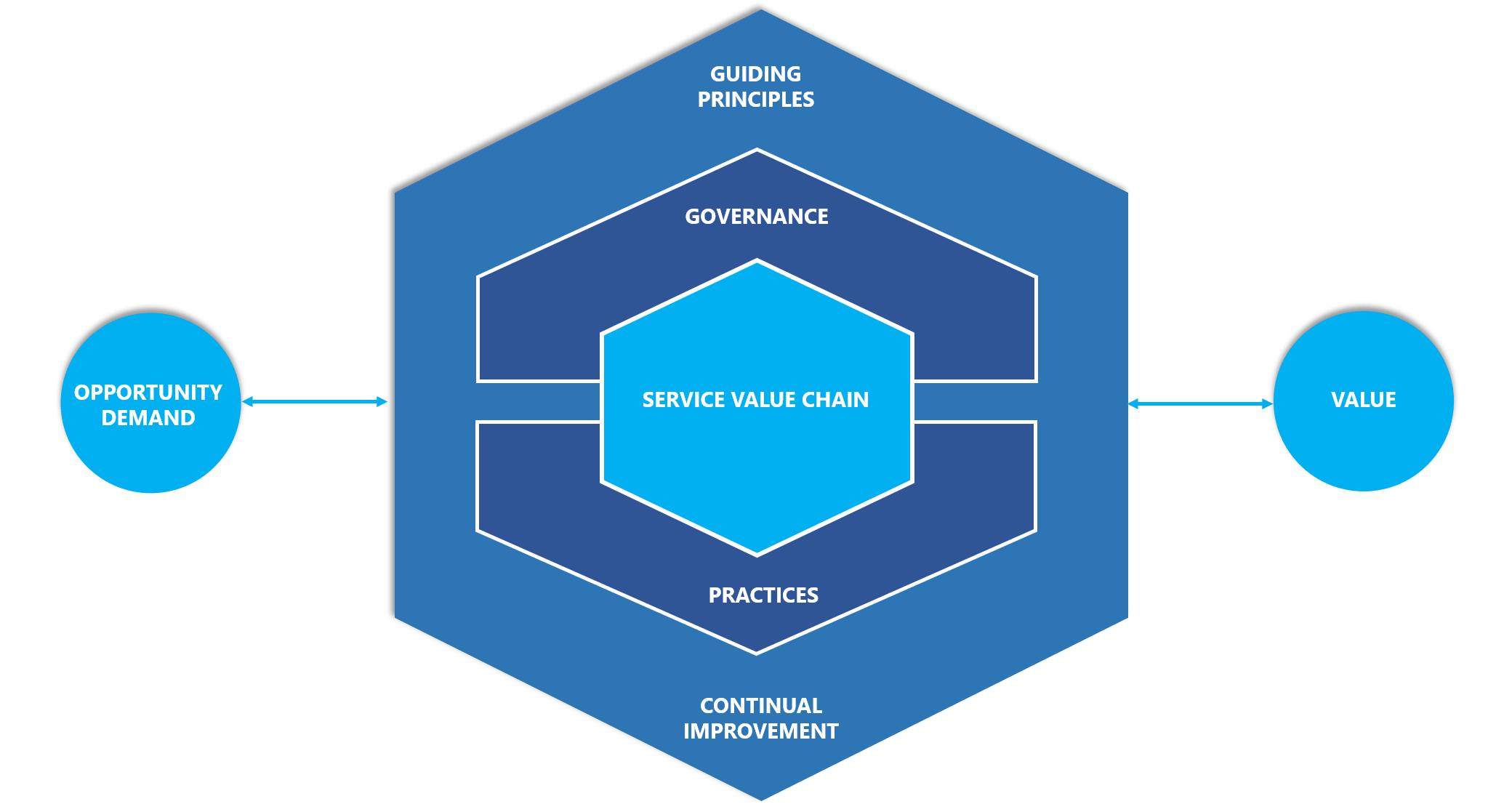
Guiding principles form the strategy laid down for the management of IT infrastructure for secure collaboration and increased business value.
Governance is a critical part and more like a Framework to align our organization with the activities. It also allows control and ensures that all activities comply with the guiding principles of ITIL framework to achieve the final goal.
The SVS is a set of interconnected activities required to realize the value and deliver results to the end-users. There are six main activities within the service value chain:
1. Plan: Involves creating a layout along with the policies to define the approach needed to achieve the organization objective.
2. Improve: Devise strategies that target to improve the practices, services, and products continually.
3. Engage: This activity will facilitate the engagement with collaborators to obtain their precise requirements and pain points.
4. Design and transition: Create new services and enhance existing services.
5. Obtain/build: Obtain customer specifications and create service modules to meet their requirements.
6. Deliver and support: Push out the services that the relevant stakeholders are using to meet their specifications.
Implement a continuous improvement process across the entire service lifecycle. ITIL 4 offers a Continual Improvement model, applied to all facets of products and services alike. However, organizations use alternative improvement approaches like Lean and Six Sigma as well.
To extract maximum benefit from ITIL, an organization need not employ all the practices. The trick to success is to use the ones that add value and align to strategic objectives.
For example, many organizations have tried to use virtualization and network transformation that needs ITIL framework, but lack of expertise has resulted in overkill at an extensive cost.