5G is revolutionizing revenue opportunities across industries. While previous network generations focused mainly on connectivity, 5G is fundamentally transforming how businesses operate and generate value. The potential is staggering – GSMA forecasts that 5G will inject $1 trillion into the global economy by 2030, creating opportunities for companies ready to innovate.
Mobile operators are backing this transformation with substantial investments. They’re getting ready to pour $180 billion into new networks in 2025. Why? They need to replace those outdated 2G and 3G systems and roll out 5G. Sure, that’s a massive investment, but they know the old networks just won’t cut it anymore.
Mobile Network Operators (MNOs), enterprises, and startups can leverage 5G for new business models utilizing its high speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity capabilities. Subsequently, they can develop cutting-edge services for various industries, effectively going beyond conventional connectivity services to become solution providers.
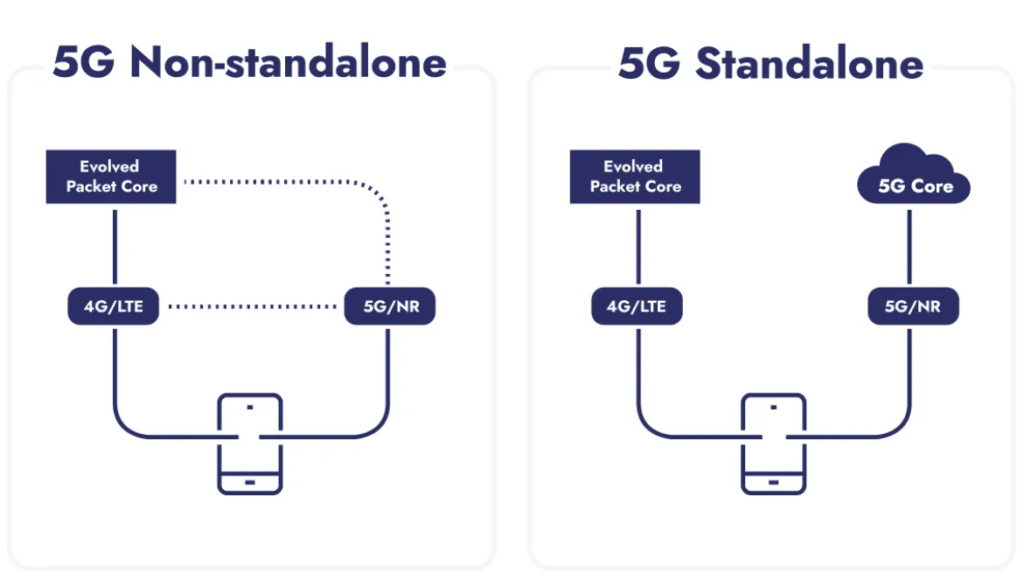
5G Standalone represents a fundamental shift in network architecture. The global market for Standalone 5G networks is experiencing rapid growth. Valued at USD 1.72 billion in 2023, it is expected to soar to USD 47.78 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 51.5% from 2024 to 2032. Conventional 5G non-standalone networks have served their purpose by leveraging existing 4G infrastructure. This dependency on legacy systems, though expedient for initial rollouts, ultimately constrains the network’s true potential.
As businesses seek increasingly sophisticated 5G applications, the need for truly independent deployment becomes clear. 5G SA steps up to meet this challenge by introducing a cloud-native core and radio architecture – independent of 4G infrastructure.
The cloud-native architecture of 5G SA makes possible to delivers advanced services with low latency and high bandwidth because of the dedicated 5G core. Hence, this allows operators to provide a end to end 5G network with enhanced user experience and network efficiency. The transition to SA architecture marks a decisive step toward future-ready networks. By breaking free from legacy infrastructure constraints, operators can finally deliver the full promise of 5G capabilities.
In addition, 5G-Advanced further expands these capabilities, opening up new monetization avenues through features like enhanced network slicing and improved reliability, paving the way for even more complex and demanding applications across various industries.
5G is no longer just about speed. Businesses are actively using it to streamline operations and generate new revenue sources. 5G is used by manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and logistics sectors to increase productivity, save expenses, and open up new business opportunities.
More flexible, usage-based strategies are replacing traditional connectivity models by businesses. Businesses may adapt connectivity to suit various requirements using Network Slicing, guaranteeing peak performance.
Edge computing further enhances processing speed, enabling real-time decision-making. Many companies now offer 5G-as-a-service, allowing businesses to scale operations without heavy infrastructure investments.
Real-time data tracking has become essential in the current scenario for factories, hospitals, and supply chains utilizing IoT sensors and AI analytics. 5G-enabled fleet tracking helps logistics companies save money on operations, optimise routes, and do predictive maintenance. For example, a logistics firm can monitor temperature-sensitive cargo in real-time and make immediate adjustments. Moreover, this increases customer satisfaction and boosts productivity.
AI-powered automation is another key factor. AI helps operators manage network performance, predict issues before they happen, and allocate resources efficiently.
This enables customers to adjust bandwidth allocation and latency, two crucial network aspects, to suit their requirements. This results in continuously better performance for gaming platforms and streaming services, allowing providers to charge based on performance.
Device status and identity verification ensure users are real, while location services assist companies in tracking and confirming device whereabouts. Furthermore, these characteristics make them useful for sectors like banking and e-commerce since they promote fraud prevention and compliance.
Though 5G offers enormous revenue-generating potential, determining the right sources and who owns them is challenging. Deploying 5G standalone networks and their fully virtualized, cloud-native designs will result in high capital and operating costs and has associated challenges that need to be addressed alongside:
A staggering 46% of telecom providers worry their businesses won’t be sustainable beyond the next decade if they stick to their current path. Why? The cost of 5G deployment is enormous—new base stations, backhaul links, cloud-native systems, and software upgrades don’t come cheap.
Getting new subscribers isn’t easy—or cheap. The intense competition in the telecom space makes customer acquisition expensive, with no guaranteed returns in the early stages of 5G adoption.
5G is a beast compared to its predecessors. Many existing IT and network management systems weren’t built to handle its scale and complexity. Upgrading or replacing them? Another expensive and time-consuming challenge.
No single player can deliver a complete end-to-end 5G solution. Operators must navigate a web of partnerships, vendors, and collaborations while trying to carve out their share of the revenue pie. This interconnected approach enables the 5G ecosystem to deliver seamless services.
From traditional telecom revenue to service-based and API-driven monetization, 5G is changing the way telecom companies make money.
Telecom providers are moving beyond the traditional subscription models, instead they are developing 5G monetization models that leverage their advanced network infrastructure.
At the front of this development is network slicing, which allows service providers to design virtual networks specifically suited to business needs. Network slicing has replaced the outdated one-size-fits-all strategy, allowing telecoms to provide tailored services and bill businesses based on their needs.
Telecoms are also evaluating API-driven monetization by allowing businesses to integrate real-time analytics, security, and edge computing into their applications. This creates new revenue streams for telecom carriers and opens new opportunities. However, there is a need for standardized APIs to enhance user experience and ensure accurate billing and fair pricing comparisons.
In this regard, Open Gateway has been gaining a lot of traction lately. It is an API framework by GSMA that lets telecom operators offer network capabilities through Open APIs.
According to a study by GSMA, the open gateway framework accounts for over 66% of mobile connections worldwide. Open Gateway Operators collaborate to create standardized APIs, ensuring compatibility across different networks. This makes it easier for developers to build and scale telecom-powered solutions.
Open Gateway helps telecom operators generate revenue from 5G by providing businesses access to advanced network features through APIs. Consequently, these features allow companies to integrate powerful telecom capabilities without deep technical expertise. By tailoring network resources to individual client needs, providers can command premium pricing for these specialized services.
5G is more than just faster connectivity—it’s reshaping industries. Going beyond typical telecom services, standalone 5G and 5G-Advanced are opening new business models. As network slicing, edge computing, and AI-driven automation mature, businesses will see unprecedented efficiencies and new 5G monetization opportunities. Hence, the introduction of Open Gateway initiatives and standardized APIs is particularly significant – these developments are breaking down traditional barriers between telecommunications infrastructure and enterprise applications. While challenges like high infrastructure costs and legacy system upgrades persist, collaboration and strategic investments will define the winners in the 5G era.
Telecom operators should embrace API-driven monetization and invest in scalable, software-defined networks. Clearly, enterprises benefit from leveraging network slicing, open-gateway and edge computing for optimized operations. The key is moving beyond connectivity—building 5G enterprises solutions that solve industry-specific problems. Undoubtedly, those who integrate 5G into their digital strategies today will lead the future of intelligent, connected industries.