The online world has changed drastically from when it first began. Today, everything you do- think communication, shopping, banking, watching movies, tax filing, buying stocks, studying- is done on the internet. And all these activities require some form of identification. This explosion of online services comes with its caveats. It is important to understand that our online data is probably as easily accessible to any hacker as it is to us. In a way, our private and sensitive information is always at stake.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a security discipline that ensures that the correct individual accesses the correct resources. It is a framework of business policies and technologies that facilitates the management of digital identities. Gartner describes IAM as a discipline that” enables the right individuals to access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons”. IAM acts as a gatekeeper that ensures that a user is what he claims (authentication) and is granted access (authorization) to resources based on his level of clearance and role.
Before we move any further, we must understand the meaning of authentication and authorization.
“Proves a user’s identity. It is based on the idea that each user will have unique information that sets them apart from other users to provide proof of identity. There are four primary types of authentication methods: static passwords that remain active until they are changed or expired; one-time passwords, such as codes delivered through SMS texts or tokens used for each access session; digital certificates; and biometric credentials.” (Source: Identity Management Institute)
All authentication methods require some verifiable information to be authenticated. There are three different categories of verifiable information:
Some of the most well-known authentication methods are –
It is not necessary that 2FA or MFA is more secure than SFA. Generally, passwords are the most common verifiable information used in SFA and are easily forgotten or compromised. On the other hand, fingerprints are also used in SFA and are one of the safest methods as they are difficult to fake. So, the security majorly depends on the type of factor/s used to authenticate.
Choosing an authentication method aims to strike a balance between security and user experience. MFA with fingerprint or facial recognition might seem like the safest bet, but it is expensive and requires the users to possess the technology to implement it. Similarly, SFA might be the best bet if not protecting sensitive information as it is cheaper and easier to implement.
“The process of granting or denying a user access to system resources once the user has been authenticated. The amount of information and services the user can access depends on the user’s authorization level.” Source: Identity Management Institute
Let us understand this with an example- Say you have to check into a hotel-
There are many ways to authorize access. 3 of the most common ones are:
Identity and access management (IAM) becomes even more necessary as cyber threats and privacy concerns rise. According to a Forrester estimate, 80% of data breaches are connected to compromised credentials like passwords, tokens, keys etc. IAM creates a security layer between the users and enterprise application, thus protecting against external and on-premises threats. It provides a centralized platform to manage identities for an enterprise and helps enforce access policies across devices and applications. It can also track user activities on company devices and enforce regulatory compliance.
(READ: Managing Enterprise Mobility Through Mobile Device Management)
The several benefits of IAM are as follows:
Organizations have a lot of personal data- of their employees, customers, potential clients etc. How this data is consolidated is very important and builds the basic security structure of an organization. The first step in this direction is a Centralized Identity management system.
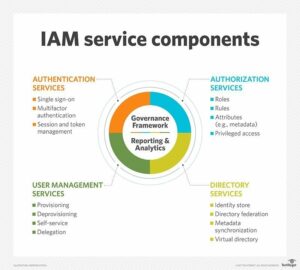
IAM can be deployed on-premises or provided by a third party through a cloud-based subscription model. According to TechTarget, IAM has four basic service components:
(READ- Security as a Service (SECaaS) – A Detailed Overview)
Centralized Identity management means all the IAM processes and data storage are done in one environment. This means users can access all the applications they need to work with the same set of credentials. As a trust relationship exists between the user, the organization and the partner applications/sites, with single sign-on in place, users can access the applications without signing into multiple accounts. For example, an enterprise can give its employees access to Salesforce, and with a single credential, the user can use the tools. This model is fundamentally built on bidirectional trust. Here the organization and Salesforce have a connection that they utilize to share information to authenticate and authorize the user.
This bi-directional trust model fundamentally differs from that used in Decentralized identity management systems. (Read more about Decentralized identity management systems)
A major drawback of Centralized IAM is that if the user credentials are compromised, the hacker can access all the information the user was privy to. This essentially means that since everything is centralized, there is a single point of failure. But strong authentication methods can easily help in mitigating the issue. HSC has been working on centralized IAM systems for quite some time now and believes its benefits far outweigh the negatives. Having a centralized IAM provides sound information security practices, efficient provisioning processes and a more accessible audit system. It also streamlines the new user creation, alteration, and termination processes. In short, Centralized IAM is here to stay.