Operator-defined Open and Intelligent Radio Access Networks, abbreviated as OpenRAN/ORAN, is the movement in mobile networks and telecommunications to improve the efficiency of RAN deployments and operations. According to Nokia, OpenRAN has been touted as the ‘next big thing in wireless’, after Massive MIMO, beamforming, 5GNR (New Radio), Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), and the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in RAN.
According to the O-RAN Alliance, the OpenRAN architecture, empowered by intelligence and openness principles, is the foundation for building the virtualized RAN on open hardware and cloud, with embedded AI-powered radio control. The architecture is based on standards defined by O-RAN Alliance, which completely support and are complementary to standards promoted by 3GPP and other industry standards organizations.
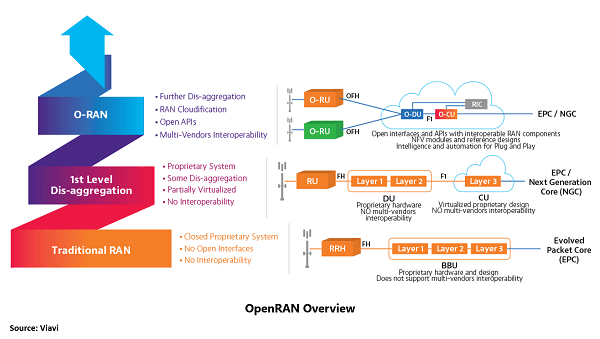
OpenRAN introduces many advantages to the enterprise telecom market, including infrastructure reconfigurability & flexibility, scalability, frequent and early deployments, higher network sustainability, and CAPEX/OPEX efficiency.
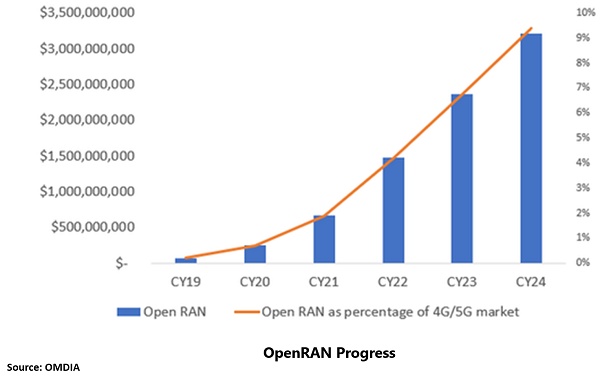
According to a report by ABI Research, the capital expenditure on OpenRAN radio units is expected to reach $47.4 billion by 2026. ABI Research expects greenfield installations and private enterprise networks, and public consumer networks in rural/uncovered areas to drive OpenRAN deployment throughout the entire forecast period.
In a 5G cloud RAN architecture, the Baseband unit (BBU) is split into two functional units, namely:
The OpenRAN concept utilizes vendor-agnostic COTS-based servers for DU and CU software to Radio Unit (RU). Let us understand the components of OpenRAN architecture:
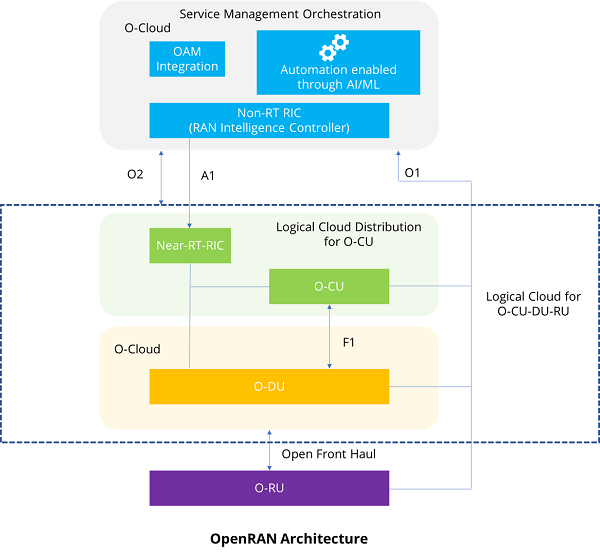
OpenRAN promises horizontal openness – with open interfaces enabling functions of the RAN to connect with other functions: Radio unit (RU), Baseband (DU-CU), CU & the NMS/orchestrator.
5G is more than RF, RAN, and Core. Machine Learning (ML) & Artificial intelligence (AI), Virtualization, Software-defined networks (SDN), Edge Computing, Management & Orchestration, etc., all contribute as the critical components in 5G.
Machine Learning & Artificial Intelligence powers the policies & rules, making them more adaptive than ever. Virtualization & SDN powers the flexibility of using COTS hardware. Edge computing gives the flexibility of deploying RAN components & network functions close to last-mile connectivity. With the introduction of microservices-based architecture and network functions distributed over different cloud/private infrastructures, the management & orchestration of the 5G networks is quite different than its previous generations.
OpenRAN is about openness and intelligence. It is about opening RAN from a closed vendor environment to a standardized multi-vendor, AI-powered hierarchical controller structure giving third-party vendor access to what used to be closed RAN data.
Traditionally ISPs were dependent on a single vendor to provide the complete RAN system. OpenRAN is bringing in the flexibility for operators to choose different components of RAN from different vendors. For example, a combination of O-CU from Vendor A, O-DU from Vendor B & O-RU from Vendor C would work seamlessly in OpenRAN architecture.
OpenRAN is revolutionizing & paving the way for transforming 5G deployment. While there will be no significant change with regards to core protocol or standard, OpenRAN would help in the adoption of innovative use cases with the architecture and openness that it provides.
OpenRAN brings in a lot of horizontal and vertical flexibility within the network, which is advantageous for the ISPs and telecom vendors. Some of the benefits of OpenRAN are:
OpenRAN is about bringing openness and intelligence into the system. It is about lowering CAPEX/OPEX for vendors, bringing in greater innovation through competition, and allowing MNOs to avoid restricted vendors. Enthusiasm around OpenRAN has been mixed as the industry is skeptical about its broader adoption, challenges with system integration, and benefits provided by OpenRAN architecture. With new players entering the telecom market and MNOs looking to develop homegrown sub-systems, there are discussions around possible use cases that can be implemented with technological evolution within 5G. OpenRAN is expected to pave the path for greater innovation and early deployment of 5G.