In the last few decades, there has been a humongous growth in the number of Internet users, devices, and connectivity-everywhere. All these factors, coupled with digital transformation across all industries globally & growing consumption of bandwidth-demanding applications, have contributed to the requirement for faster and ubiquitous wireless connectivity. To address these, the Wi-Fi Alliance- the organization responsible for conceptualizing, developing, & certifying Wi-Fi standards- announced the next generation of Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi 6. This next generation of wireless networks based on 802.11ax is a development over the current fifth generation of Wi-Fi, known as Wi-Fi 802.11ac (standardized in 2014).
Understanding Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 is an industry certification program based on IEEE 802.11ax standard. It enables the next generation Wi-Fi connectivity promising higher capacity, coverage, and performance even in hyper-dense environments. These networks enable lower battery consumption making them perfectly suited for the new-age connected applications, such as smart homes, Internet of Things, and Smart Manufacturing.
Wi-Fi 6 lays down the foundation for a multitude of uses from UHD movies streaming, high-bandwidth low-latency business applications to seamless connectivity in large & congested hyper-dense environments.
Identifying Wi-Fi 6 other Wi-Fi Generations
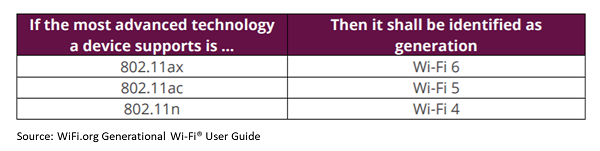
The Wi-Fi Alliance has introduced simplified generational names in the device names product descriptions. These provide device manufacturers, operators, and end-users with an easy description for both the Wi-Fi technology supported by the device along with the type of connection that it makes with a Wi-Fi network.
As defined by WiFi.org, the goals of generational Wi-Fi are:
- Increase end-user recognition of Wi-Fi technology advancements
- Differentiate and easily identify Wi-Fi technology contained in devices and network connections
- Increase user adoption of newer Wi-Fi technologies that deliver a better experience
Wi-Fi generations are now identified using a numerical sequence matched to PHY advancements in 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Key Capabilities of Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 promises a variety of improvements and fresh features that drive Wi-Fi devices towards higher operational efficiency. The improvements are made possible by some key enabling technologies that bring enhanced performance even in demanding environments. Let us have a look at them:
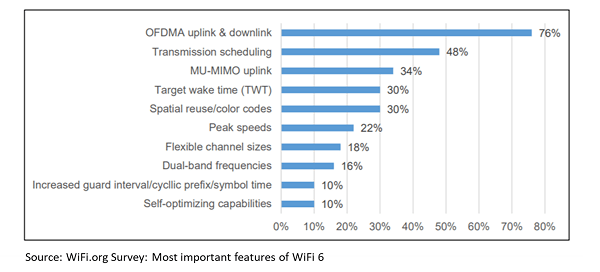
- Uplink & downlink orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA): For increased efficiency & low latency. Access Points on Wi-Fi 6 can stay connected to more devices at once.
- Multi-user multiple input, multiple output (MU-MIMO): To enable access points (APs) to handle larger numbers of devices simultaneously. It operates across the 2.4GHz & 5GHz simultaneously
- Transmit Beamforming: To enables higher data rates & increase network capacity
- 1024 quadrature amplitude modulation mode (1024-QAM): For increased throughput for bandwidth-heavy applications
Wi-Fi 6 Devices
According to a report by ABI Research, 802.11ax or Wi-Fi 6 chipsets are forecasted to reach more than a billion annual shipments by 2022, only within three years of the first commercial deployments -expected in the last two quarters of 2019. The report also mentions that,The enormous growth in Wi-Fi-enabled devices, increased per-user traffic demand, greater number of users per Access Point (AP), increased cellular offloading, higher density Wi-Fi deployments, growing use of outdoor Wi-Fi, heterogeneous device and traffic types, and a desire for more power and spectral efficiency are all major driving forces behind the introduction of 802.11ax’s/Wi-Fi 6. Currently, some of the OEMs such as Broadcom, Qualcomm, Marvell, Quantenna, Intel, and Celeno have Wi-Fi 6 pre-standard chipsets.
As per Reuters, in 2018, the telecommunications regulator FCC voted in favor of opening 1200 MHz of spectrum for unlicensed devices in the 6GHz band. The 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6 working committee is now looking for ways to incorporate the 6GHz support into 802.11ax. The availability of spectrum would facilitate smoother adoption of 6GHz devices.
Backward compatibility with previous Wi-Fi generations
Wi-Fi 6 is adaptable and designed for both forward and backward compatibility. Wi-Fi 6 clients would not necessarily require upgrades in the existing legacy infrastructure.
According to WBA Alliance, Wi-Fi 6 supports both 2.4 and 5 GHz wireless devices. Thus, 802.11a/b/g/n/ac devices will be able to co-exist with the new Wi-Fi 6 devices. For backward compatibility, Wi-Fi 6 radios also support OFDM and HR-DSSS.
Benefits of Wi-Fi 6 technology
Wi-Fi 6 brings in significant improvements through key enabling technologies such as MU-MIMO & OFDMA to achieve faster and highly optimized Wi-Fi performance. Let take a closer look at some of the advantages of using Wi-Fi 6 technology:
- Increased capacity and higher data rates: With 1024QAM, Wi-Fi 6 can deliver a 25% increase in capacity over 256QAM, as in previous Wi-Fi generations, particularly at close distances./li>
- Simultaneous Multi-user operations: Wi-Fi 6 is capable of reducing congestion in the network by allowing more devices to connect. It is enabled throughMU-MIMO technology and OFDMA.
- Improved power efficiency: Target Wake Time (TWT), a feature in Wi-Fi 6 networks, lets routers schedule check-in times with devices. This allows devices to plan communications with a router in advance, thus reducing the amount of time they need to keep their antennas powered on to transmit and search for signals. It improves the battery life of devices and routers for low-power Wi-Fi devices. The TWT mechanism was originally introduced in the IEEE 802.11ah amendment.
- Performance in hyper-dense environments: Multiple Access Points deployed in dense device environments can collectively deliver the desired QoS to clients with diverse usage profiles in Wi-Fi 6. It can significantly increase the aggregate wireless network throughput to address high-density venues such as stadiums, auditoriums, retail chains, and malls, etc.
Deployment Scenarios
Here are some of the deployment scenarios of Wi-Fi 6:
Public Venues/Stadiums/Entertainment Parks
Public Venues such as Airports, convention centers, Railway & metro stations, etc receive a high footfall every day and thus, the population density at these venues is very high. This requires the BSS at these places to support a high network bandwidth requirement from users.
Wi-Fi 6 technology improves the efficiency of the spectrum, thereby enabling concurrent usage and increased bandwidth requirements. Since the venues may experience a sudden rise in voice traffic (carrier offload) on Wi-Fi networks, Wi-Fi 6 can handle latency efficiently. Wi-Fi 6 uses OFDMA, MU-MIMO for uplink & downlink which helps support the increasing demand for video content uploads/downloads from users in a hyper-dense environment.
Industrial IoT
The Wireless Broadband Alliance Mettis Aerospace announced the world first Wi-Fi 6 Industrial Enterprise and IoT trial. The use cases under this alliance include multi-stream live video monitoring, real-time energy monitoring, ultra-reliable low latency communications with sensors on critical systems, and augmented reality.
Smart Cities
The capabilities of Wi-Fi 6’s in terms of high capacity support and increased throughput have significant benefits for deployment in Smart Cities. The increased throughput through Wi-Fi 6 is significantly important for enabling wireless backhaul scenarios for the Smart Cities network.
Congestion planning for smart cities network can be simplified through the use of Wi-Fi 6. The benefits of the frequency re-use features in Wi-Fi 6 facilitate spatial efficiency and allow access points to be moved closer. This increases the overall network capacity with a higher density of access points for a given number of users inside a cell.

 Product Engineering Services Customized software development services for diverse domains
Product Engineering Services Customized software development services for diverse domains
 Sustenance Engineering Going beyond maintenance to prolong life of mature products
Sustenance Engineering Going beyond maintenance to prolong life of mature products
 Managed Services Achieve scalability, operational efficiency and business continuity
Managed Services Achieve scalability, operational efficiency and business continuity
 Technology Consulting & Architecture Leverage the extensive knowledge of our Domain Experts
Technology Consulting & Architecture Leverage the extensive knowledge of our Domain Experts