In an era of unprecedented digital connectivity, efficient wireless communication is of high significance. As the number of devices connected to a network increases, traditional static radio becomes inadequate with increasing interference and reduction in signal quality. This is where cognitive radio gains significance in wireless communication with the capability to dynamically manage frequency spectrum.
Cognitive radio networks are intelligent systems that automatically detect unused radio channels and shift the transmission and reception parameters to utilize the spectrum more efficiently.
They are an extension of software-defined radio, which uses software instead of conventional hardware to perform radio-signal processing functions. Software-defined radio can receive and transmit different radio protocols by changing the software and can extend the radio’s capabilities without modifying the hardware.
Cognitive digital radios perform spectrum sensing to continuously scan the radio environment to identify unused channels and avoid occupied channels. They can seamlessly transition across different frequencies to utilize unused frequencies for optimum performance. Additionally, they can manage the available spectrum by dynamically utilizing and sharing it intelligently.
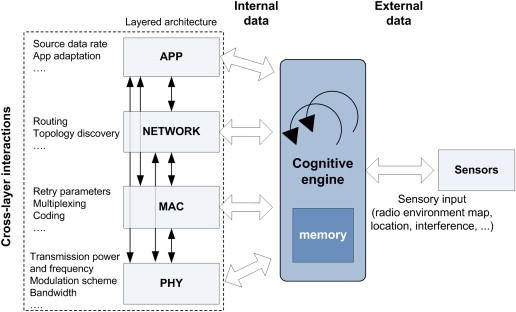
The cognitive engine contains a decision-making process which is usually implemented using machine learning. The engine considers the various inputs like geographical and operating environment, expected performance metrics and available radio configurations as input. It uses sensing techniques like Fast Fourier transform to detect the signal strength level in the spectrum band and maps this sensory data into the machine learning model. Based on these inputs, it decides the best radio configuration to be implemented. Cognitive radio systems can reconfigure the parameters like transmitted power, sampling rate, centre frequency, or waveform dynamically and autonomously.
Additionally, they also have a feedback loop using which it can learn from experience and experiment with new configurations in new situations. They identify new problems and store the related new solutions in the database. These systems use reinforcement learning to learn and gain experience. These utilize the output of the previous action to influence the future decision making. For some applications, neural networks are also used within the reinforcement learning framework to train the model.
Cognitive digital radios form relationships between different parameters, which describe how modifying the different parameters achieves the objective. Each networking experience is described using mathematical relationships that relate to device configuration and environmental parameters. This describes the degree of achievement of the objective and leads to the final decision for transmission. All cognitive radio applications operate in different environments and have different requirements. A solution for an application may not yield acceptable performance when applied in different environments.
The cognitive decision-making process takes its inspiration from the behavioral model of a bumblebee. The bumblebee has the characteristic of a social animal that exchanges information with each other to perform an action to achieve the best result. A cognitive model of the bumblebee was ideal as it is socially independent by nature. It collects information from the environment and shares it with other bumblebees but makes decisions without control from the collective. The Bumblebee behavioral model is well suited for operating environments where network topology changes frequently. It is also suited in environments where channel conditions and spectral availability change as a function of time with a changing number of radios as a part of the network. It is also suitable for the radio to gather information about the environment and then act to enhance its own performance.
Source: sciencedirect.com
Radio Frequency spectrum is a limited resource usually allocated by governments. As the number of devices and services grows, cognitive radios efficiently utilize the available spectrum.
As devices utilize the same frequency bands, there can be interference in the transmission. Cognitive radio intelligently adjusts the parameters to minimize overlap in frequency and maintain clear communication.
Furthermore, these can support a higher number of users and more data-intensive applications, which is essential for advanced use cases.

Firstly, these radios can manage and plan the available spectrum effectively to reduce interference between systems. Secondly, they ensure minimization of idle or underutilized frequencies through real time monitoring and adjustment of spectrum usage. It also enables sharing of spectrum among multiple communication systems. Lastly, these enhance the efficiency of the spectrum and reduce the cost of additional infrastructure by better utilizing existing spectrum.
Cognitive radios improve the quality of service with high data rates, reduced interference, bit error rate and power consumption. They also accommodate a greater number of users within the same network. Moreover, they also provide ability to switch between different networks to enhance connectivity.
The authority assigns spectrum bands to licensed users in a particular region. A large portion of assigned spectrum is sporadically used with high variance in time. Some governments allow the usage of unutilized spectrum by secondary users. Cognitive radios continuously monitor the spectrum to detect the channel used by the primary users. This enables secondary users to access the unutilized spectrum without causing interference to the primary users.
Cognitive radios enable vehicular adhoc networks (VANETS) which supports Vehicle to vehicle and Vehicle to infrastructure communication. They enable vehicular communication systems that can network on the road in real time. VANET offers services like traffic control, entertainment, safety applications, driving assistance, collision avoidance, and safety services.
Furthermore, these have a wide range of application in IOT systems like smart homes, automated factories, and intelligent buildings. Conventional systems face challenge in achieving reliable communication due to extremely crowded frequency bands. Along with this, cognitive radio networks can manage the spectrum to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
For real time surveillance systems require high reliability and small delays due to network issues can be critical. Cognitive radios can switch to different channels with better conditions. In addition, they can use channel aggregation and multiple channels to improve performance.
Cognitive radios find wide range of military applications like command and control operations, intelligence assistance, targeting etc. Also, they are useful for switching bands when adversaries use jamming signals to interfere with communication.
5G radio spectrum sensing identifies and classifies signals. This can reduce interference in the network and improve the efficiency of energy utilization. Cognitive radios provide efficient and accurate spectrum utilization.
Cognitive radio is playing a key role in overcoming the challenges of spectrum scarcity and enhancing wireless communication. It enhances efficiency and connectivity and manages radio frequency in an intelligent manner. The ongoing advancements in technology will lead to cognitive radios meeting the current demands and will also drive future innovations in telecommunication.