6G is the sixth-generation mobile system standard for wireless communication technologies. In India, it is seen as a catalyst for the nation’s digital transformation, offering greater frequencies than 5G networks, higher data capacity, and significantly lower latency. As wireless networks get closer to 6G, the convergence of digital and physical realities will become imperative.
Core Goal of the 6G Vision
The 6G vision is to establish a seamless ecosystem where the physical and digital worlds merge. This integrated world will provide new and innovative methods to communicate by providing intelligent solutions. Its objective is to create a society that is more efficient, sustainable, and human-friendly. By bridging the gap between artificial intelligence and telecommunications, 6G will build a world in which everything is sensed, connected, and intelligent.
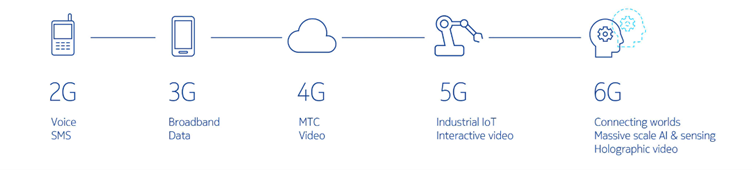
Source: Nokia
Building upon the current 5G technology, 6G will offer speeds almost 100 times faster, providing unparalleled reliability and ultra-low latency. These advancements will not only transform the daily lives of consumers but will also impact the economies at large while mitigating the carbon footprint and energy consumption.
Advancements and Promises of 6G
Each generation of communication technology has brought about a shift in the network focus. 2G and 3G networks prioritized human-to-human communication through voice and text. 4G revolutionized seamless streaming and massive data consumption. 5G technology focuses on the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, smart solutions, and automation. With 6G, we can expect an amalgamation of digital, physical, and human worlds, delivering intelligent solutions on an unprecedented scale.
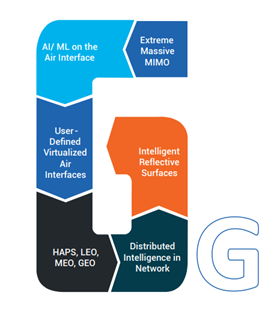
6G Network Architecture
Successful implementation of a network supports cloud infrastructure, AI/ML capabilities, and ultra-high speeds with security requires innovative architectural designs. A key feature of 6G networks is that their architecture should be designed to handle communication, computation, caching, and control (C4) resources as a unified system. Factors like capacity, throughput, reliability, latency, scale, flexibility, sustainability, digital inclusion, security and privacy will play a role in 6G’s design principles. The architecture will have to be customizable and specialized so that it can be deployed in large-scale as well as in a personal setting.
6G Spectrum Allocation
Spectrum allocation is vital for radio connectivity. Each new mobile generation requires access to new spectrum bands to leverage the benefits of the new technology innovations fully. The 7–20 GHz spectrum is essential for providing extreme wide area capacity, while the 92-300 GHz is needed for the highest peak data rates and sensing.
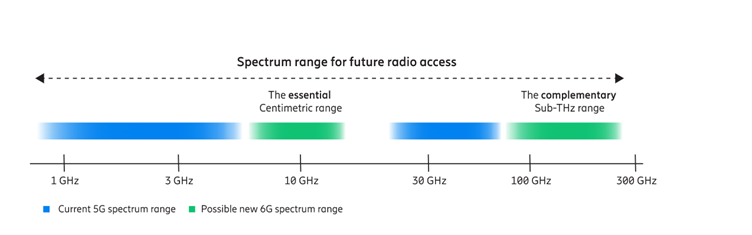
Spectrum range for future radio access
Source: Ericsson
Potential 6G Use Cases
6G will unlock innovative, futuristic use cases that will transform our lives and industries. Some of the potential use cases are:
• Revolutionize Industry 4.0:
6G networks will support new types of intelligent machines that will be able to communicate with each other without much human intervention and help revolutionize the Industry 4.0 landscape.
• Augmented and Virtual reality:
With 6G, powerful sensors will enable the creation of digital assets based on real-life objects and people, transforming the business and entertainment world.
• Ehealth:
Remote surgeries and the availability of telepresence tools will guarantee healthcare workflow optimizations for patients.
• Unmanned mobility:
It will enable autonomous transportation systems focusing on passenger safety and optimizing traffic management.
The Indian Story After 25 Years of Internet
India went from a country with less than 2 crore landline connections (in 1998) to more than 70 crore active internet subscribers today with 75% of them always having internet connectivity irrespective of their location and this number is expected to grow to 90 crores by 2025. During the last five years, India has also boosted telecom equipment manufacturing and exports in a major move towards an Aatmanirbhar Bharat, a.k.a, A self-reliant nation.
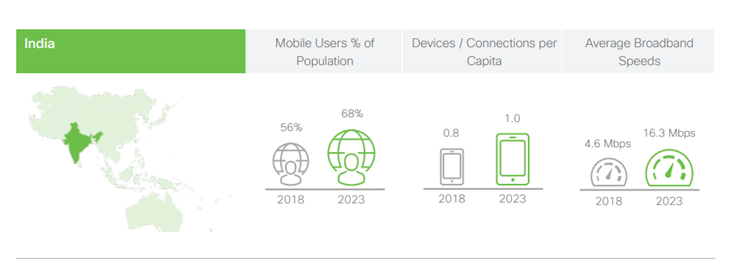
Source: Cisco
At present, the total annual purchase of smartphones is greater than 16 crore smartphones for about 30 crore Indian households. This means that every household today is buying smartphones at an average of one phone every 2 years and affordable telecom technology has enabled Indian citizens to develop their lives and livelihoods at a speed unseen in previous generations.
Bharat 6G - Deployment of 6G in India
By promoting 6G research and innovation domestically, the government hopes to make India a world leader in 6G technology and manufacturing by the year 2030. This will allow India to become more than just Aatmanirbhar but also a significant contributor to the world.
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has constituted a technology innovation group on 6G (TIG-6G) with representatives from various ministries/departments, research and development organizations, academic institutions, telecom service providers and industry to develop a roadmap and action plans for 6G deployment in India.
The vision of the Bharat 6G states to design, develop and deploy 6G network technologies that provide ubiquitous, intelligent, and secure connectivity for high-quality living experience for the world.
Indian researchers are confident that the 6G technology in India will be rolled out using indigenously developed hardware and software that can also be exported to other countries.
The Global Race towards 6G
As of 2023, the estimated number of internet users worldwide is 5.16 billion, up from 5.06 billion in the previous year. This share represents about 65 per cent of the global population.
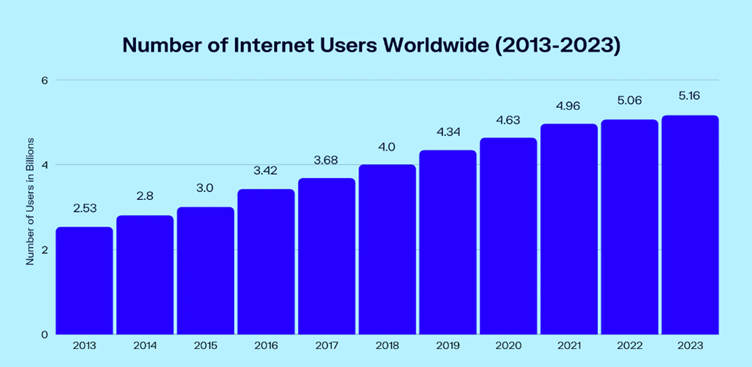
Source: Oberlo
The global ambition is to change further connectivity such that big data analytics and holographic displays become the standard. Various countries, including China, the United States, Japan, and South Korea, are investing substantial sums of money in the study of 6G technology. Researchers are concentrating on ensuring that people, organizations, and governments can completely rely on future networks to be safe, dependable, and accessible at all times.
Another focus is on the need for distributed cloud providing increased flexibility and performance. Japan and South Korea are focusing on Edge computers that will be capable of Artificial Intelligence.
Looking at the industry, Nokia is currently leading project Hexa-X, Europe’s premier 6G research initiative, while Ericsson manages the technical aspects of the program.
It is exciting to think about what lies ahead and great to see many leaders in Big Tech and countries, especially India making the right noises about 6G.

 Product Engineering Services Customized software development services for diverse domains
Product Engineering Services Customized software development services for diverse domains
 Sustenance Engineering Going beyond maintenance to prolong life of mature products
Sustenance Engineering Going beyond maintenance to prolong life of mature products
 Managed Services Achieve scalability, operational efficiency and business continuity
Managed Services Achieve scalability, operational efficiency and business continuity
 Technology Consulting & Architecture Leverage the extensive knowledge of our Domain Experts
Technology Consulting & Architecture Leverage the extensive knowledge of our Domain Experts